WAVES
Scenario-based learning (SBL) techniques are widely recognised as a key tool in the educational toolkit, for safe training in competency and decision-making, but the available applications are challenging for educators to understand and use without considerable resource and effort.
This project combines skill sets of both academic and enterprise partners to make SBL more accessible for a wide range of professions. Developments will include the ability to embed SBL activities directly into learning platforms and Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs). By embedding SBL, MOOCS will enable development of real world skills, competency and experience rather than knowledge. The provision of training materials in multiple languages, including a ‘How to create Virtual Scenarios’ MOOC, will make VS more accessible for educators. The project will sustain and disseminate these activities through an extended partnership, the ‘WAVES’ network.
Objectives:
- Develop and make accessible to the wider educational community, scenario-based learning (SBL) applications to promote new learning and teaching methods
- Extend massive courses, replacing their oversimplified assessments and activities, with learning activities that are more engaging and authentic
- Share knowledge and provide end-user support guides and training, to reach a critical mass of learning resource creators and a large end user audience
- Impact different professional groups and networks linked to the partners, through both direct involvements and responsibilities within those groups or networks, or through a series of engagement/dissemination events, and processes.
More info here.
TAME 
The overall objective of this project is to introduce innovative pedagogy methods that will provide training for students against medical error. TAME will innovate curricula towards teaching and learning in safe environment and closer to the needs of the real practice, where medical errors occur.
Objectives:
- Develop a Virtual Patient methodology based on virtual case histories to enable future physicians to avoid most common medical errors in the diagnostic and therapeutic process on a safe environment, before exposure to real patients.
- Transfer knowledge and experience from the institutions which have already gone through a successful implementation of learning methods in paediatrics; develop Paediatric (modules) in each institution as exemplar studies.
- Use the experiences gained in the exemplar study to create similar resources in different clinical attachment areas in each institution.
- Use supra-regional ePBLnet, MEFANET, and other medical education networks to create, share and disseminate these multi-lingual, multi-cultural resources aimed at avoiding or decreasing medical errors.
More information here.
MEDCIN
There is an ever increasing need for standardised curricula in medical education, particularly within the EU. The need for free movement of skilled workers and the demands of the Bologna Process require a consistency of approach by higher education institutions to ensure that learners have a shared level of knowledge. A comprehensive platform that would provide the necessary instruments for easy in-depth curriculum management is required, but no suitable platform is currently available. For any platform to achieve these goals, it is essential that data standards be used to enable the systems to communicate across organisations and implementations.
The need for standardized curriculum particularly in medical education is indispensable. Today a comprehensive platform that would cover all necessary instruments for easy in-depth curriculum management is still missing. For any platform to achieve these goals, it is essential that data standards are used to enable the systems to communicate across organizations and implementations.
MEDCIN proposes an innovative methodological background including web-based visualization tool for comprehensive evaluation and map of medical curricula with the use of modern information and communication technologies. We aim to identify and validate novel, potentially useful patterns, which will significantly help curriculum managers/evaluators to make right decisions, and afterwards build a well-balanced medical curriculum.
The project will be based on the MedBiquitous Consortium, the leading organization in the development and promotion of technology standards for the health professions.
Objectives:
- Standardize medical curriculum management system (OPTIMED platform)
- Propose innovative methodological background to evaluate and map medical curricula
- Build an original model to compare medical curricula
- Foster increased awareness of existing educational standards produced by MedBiquitous
- Provide an exemplar implementation for dissemination of best practice.
More information here.
MOOCs
MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses) are free online courses upon which anybody can enrol, regardless of their academic background and prior knowledge. Often developed by leading academic institutions, MOOCs can integrate a range of eLearning tools, including social networking, videos and quizzes, in order to create engaging, appealing and often educationally innovative online learning experiences. Statements of Participation and Certificates of Achievement can be purchased by learners to recognise their completion of a course.
The eLearning Unit has been developing MOOCS in collaboration with FutureLearn (www.futurelearn.com), a MOOC platform that focuses on social learning and the use of storytelling as an educational tool. FutureLearn has a large number of both UK and international partners providing courses, and a learner base of more than 2 million.
Our current MOOCs:
1. The Genomics Era: the Future of Genetics in Medicine

Brief Description: This free online course is aimed at healthcare professionals, giving them the basics of genomic medicine and demonstrating the growing role of genomics in healthcare, both for patient diagnoses and treatment.
Main objective: To develop an engaging, freely available online teaching resource that can upskill the healthcare workforce in the use of new technologies in genomic medicine.
2. ECG Assessment: an Introduction for Healthcare Providers
Brief Description: This free online course is aimed at healthcare professionals, aiming to equip them with a basic understanding of ECG assessment and interpretation, which will support the further hands-on training that is needed to competently perform the ECG test in clinical settings.
Main objective: To develop an engaging, freely available online teaching resource that can up skill the healthcare workforce with an introductory understanding of ECG assessment and interpretation.
CROESUS 
CROESUS trains academics and students to create their own learning and teaching content and introduce interactive patient systems as well as innovative pedagogy methods in the form of VPs into the clinical elements of the course. It transfers knowledge from leaders in virtual patient (VP) development and effectively implements VPs in the medical curriculum of the participant institutions – Masaryk University (Czech Republic) and Univerzita Pavla Jozefa Safarika V Kosiciach (Slovakia). It engages with other partners and networks, particularly the MEFANET network, to increase the use of such platforms and methodologies in the wider community. Importantly, it presents these within the culture and languages of the participant countries.
Objectives:
- To introduce innovative pedagogy methods using scenario-based learning tools, virtual cases and patients thus to enable future physicians and healthcare professionals to simulate important steps in the diagnostic and therapeutic process before exposure to patients.
- To transfer know-how and best practices from the institutions which have already gone through a successful implementation of authentic, motivating, competency-based learning styles into the medical curriculum.
- To link with the existing regional (Czech/Slovak) medical education network MEFANET and other European projects with similar objectives and use this wide community of students and teachers to disseminate the patient cases and project’s outputs more widely.
More information here.
 ePBLnet
ePBLnet
ePBLnet is a Tempus funded, supra-regional programme to  modernise medical education in Georgia, Ukraine and Kazakhstan, and build a network across Eastern and Western Europe.
modernise medical education in Georgia, Ukraine and Kazakhstan, and build a network across Eastern and Western Europe.
Objectives:
- Establish a Supra-Regional Network based on three national medical education centres (MECs) in Georgia, Ukraine and Kazakhstan.
- Use MECs to modernise the teacher-based and classroom-orientated medicine course in six universities, with a focus on competence-based learning, built around Problem-Based-Learning (PBL) and Virtual Patients.
- Link with other medical education networks with similar needs for modernisation and cultural preservation.
- Use this network to generate the critical mass of institutions needed for sustainable development.
- Focus this development through self-funded ePBLnet conferences and workshops beyond the project lifetime.
More information here.
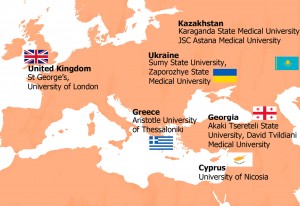 Partners:
Partners:
- St George’s, University of London
- Aristotle University of Thessaloniki
- University of Nicosia
- Karaganda State Medical University
- JSC Astana Medical University
- Zaporozhye State Medical University
- Sumy State University
- David Tvildiani Medical University
- Akaki Tsereteli State University
Electronic Virtual Patients (eViP)
 eViP is a programme co-funded by the European Union to create a bank of repurposed and enriched multicultural Virtual Patient cases from across Europe which have been made available under a Creative Common Licence.
eViP is a programme co-funded by the European Union to create a bank of repurposed and enriched multicultural Virtual Patient cases from across Europe which have been made available under a Creative Common Licence.
 St George’s, University of London was the lead co-ordinator for the eViP programme. The e-Learning Unit led the pilot study and the overall management of the programme.
St George’s, University of London was the lead co-ordinator for the eViP programme. The e-Learning Unit led the pilot study and the overall management of the programme.
More information here.
More information about the pilot study here.
Repurposing Existing Virtual Patients (REViP)
 REViP is a one year project co-funded by the JISC to explore and evaluate the embedding of repurposed and enriched Virtual Patients (VPs) within a Paediatrics component in the St George’s medical curriculum.
REViP is a one year project co-funded by the JISC to explore and evaluate the embedding of repurposed and enriched Virtual Patients (VPs) within a Paediatrics component in the St George’s medical curriculum.
Major outputs: Six openly available VPs and a video case study outlining the repurposing process from Germany to the UK
Key outcome: ![]() repurposing proved an efficient process for transforming content from one healthcare culture to another if structures of the cases were similar.
repurposing proved an efficient process for transforming content from one healthcare culture to another if structures of the cases were similar.
More information here.
mEducator
The mEducator Best Pra ctice Network (BNP) aims to implement and critically evaluate existing standards and reference models in the field of e-learning in order to enable specialised state-of-the-art medical educational content to be discovered, retrieved, shared and re-used across European higher academic institutions.
ctice Network (BNP) aims to implement and critically evaluate existing standards and reference models in the field of e-learning in order to enable specialised state-of-the-art medical educational content to be discovered, retrieved, shared and re-used across European higher academic institutions.
More information here.
